Americans discard 7.8 billion at-home generated sharps each year — and that does not include healthcare facilities! With high production of medical waste comes a critical next stage to consider: the medical waste disposal lifecycle. We know that without proper containment, the medical waste disposal lifecycle fails. Here is a peek into what happens between the time of injection (either at-home or at a healthcare facility) and the disposal process.
Phase 1: Producing
- Biomedical waste is any kind of waste containing infectious (or potentially infectious) materials. This includes sharps, which is a medical term for devices with sharp points or edges that can puncture or cut the skin. Examples of sharps include: needles, syringes, lancets, auto injectors, infusion sets, and connection/needle sets.
Phase 2: Storing
- Whether someone is at home, or in a healthcare facility, proper storage and containment of biomedical waste is essential to protecting our communities and environment. For instance, proper sharps disposal requires used sharps be placed in an FDA-cleared, puncture-proof container labeled as biohazard waste. If a patient is performing at-home injections, it’s important they follow their states’ Sharps Disposal Guidelines.
Phase 3: Treating
- Once the biomedical waste has arrived at the waste treatment facility it is sorted and prepared for disposal. The most common way to treat biomedical waste is via autoclave, a machine that uses high pressure steam to kill pathogens. For medical waste that does not get treated by autoclave, incineration is used. This method turns waste into ash, hindering harsh chemicals from getting into waterways.
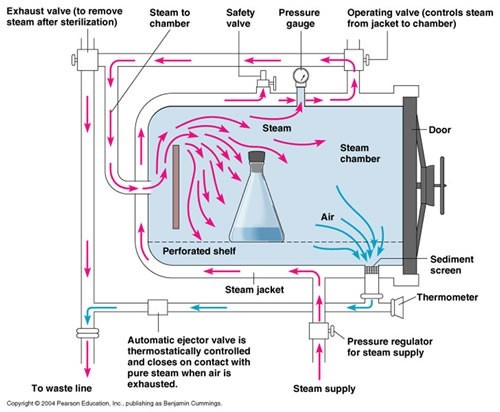 Process by autoclave.
Process by autoclave.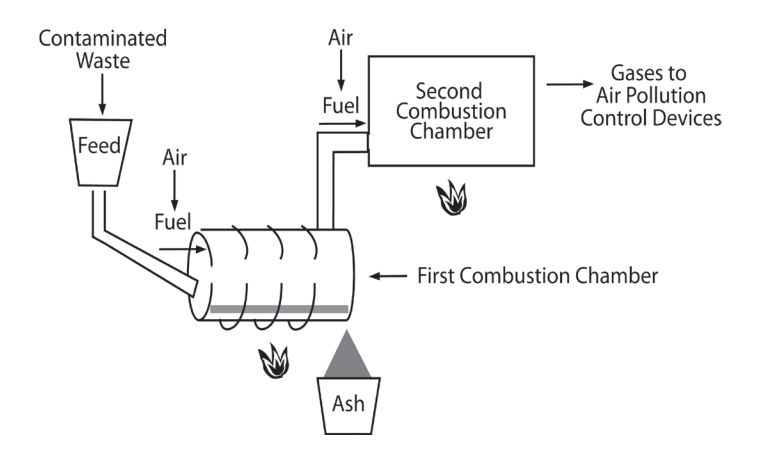 Process by incineration.
Process by incineration. Phase 4: Disposing
- Depending on local and state regulations, the final disposal phase can occur in one of two ways: It will either be sent to a landfill, or sent to a waste-to-energy facility. If sent to a waste-to-energy facility, the medical waste will be converted into clean energy. This energy can be used in our communities, our homes, or by the waste treatment facility to help run equipment.
At UltiMed, we focus on sharps lifecycle management solutions, helping to ensure safe sharps disposal guidelines are met across the country. Our patented and proprietary UltiGuard® Safe Pack is the only all-in-one solution to conveniently dispense and safely contain sharps for proper disposal, all in one easy-to-use system.
Within the medical waste disposal lifecycle, the UltiGuard Safe Pack streamlines Phase 2 for at-home injections, and is compliant with Sharps Disposal Guidelines in all 50 states. Additionally, the UltiGuard Safe Pack is available in a variety of sizes for both pen needles and insulin syringes.
Choosing UltiGuard Safe Pack helps protect your community, safeguard medical waste workers, and remove medical waste from the environment. UltiGuard Safe Pack has helped over 900 million pen needles and syringes be disposed of safely since 2010.
Sources: PRWeb, Vanderbilt.edu and Pureway.com